Spectrometry with your microscope!
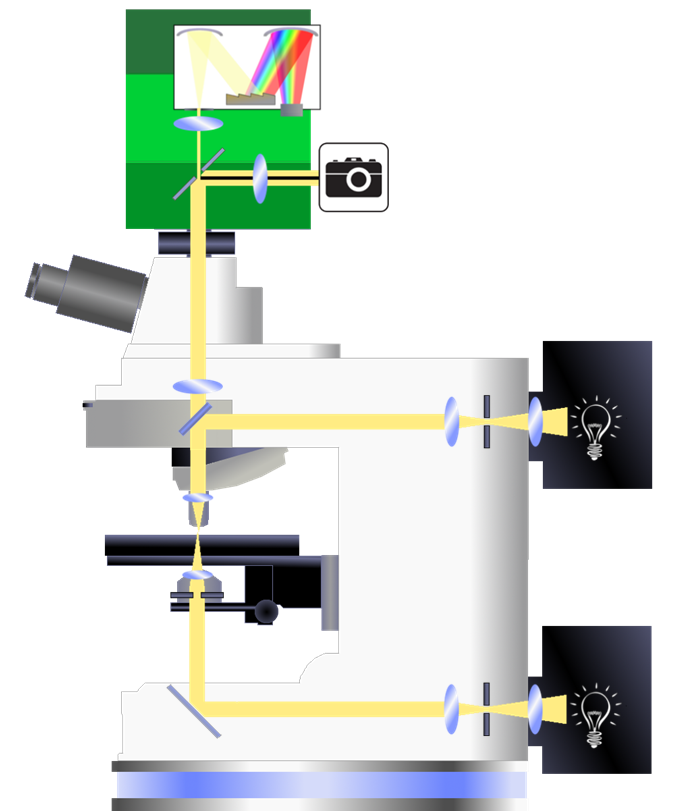
As shown in the diagram on the right, the MSP head unit can be added to the photoport of a microscope, and the spectrometer measures the light that is collected by the objective and focused onto the spectrophotometer entrance aperture. Whether this light is transmitted through the sample, reflected from the sample, or emitted by the sample, that only changes the calculations done on the light intensity measured.
Beyond just measuring UV-VIS-NIR spectra with microscale sampling areas, microscope spectrometry is also capable of microspot thin film thickness and colorimetry measurements. When combined with motorized stages, hyperspectral data cubes can even be created with various types of spectra. Because these instruments are so flexible, MSP's are used in many diverse fields of research and industry.
Relative Intensity Measurements of Displays
![]()
Figure 1: Microspectrometers are used to measure the intensity of each pixel
![]()
Figure 2: Typical test spectra from a display. Intensities can be directly compared between pixels.
The luminance, intensities or brightness of individual pixels and groups of pixels can be measured and compared using microspectrometers.
Flat panel displays consist of a series of colored lighted areas arranged in a pattern and can only be readily viewed with magnifying optics. Due to the high resolution of flat panel displays, they are manufactured with hundreds of rows of microscopic "pixels" on a surface. Generally, these pixels are red, blue and green though pixels with other colors are also made...for example the latest four color systems also incorporate yellow pixels.
One aspect of display quality control consists of making sure that the brightness or intensity of each pixel does not vary across the entire display. For example, all the green pixels should have the same brightness no matter where they are positioned in the display.
Microspectrometers are able to gather relative intensity data from single pixels and from groups of pixels (if you are interested in mura). Additionally, microspectrometers are also able to map the relative intensity variation within even a single pixel! This leads to a new level of precision for improved displays.
The way a microspectrometer works is that spectrophotometer entrance aperture is placed over the pixel or pixels in questions. The black square in Figure 1 is an example. The spectra is then acquired and will look something like the three spectra in Figure 2. Using the LambdaFire™ software, the intensity data is compared with measurements of other pixels to show that the brightness of each sampled area is within the manufacturing parameters. A high resolution map of the relative intensities can then be generated.
Learn more about relative intensity measurements of displays below:
Microdisplay Inspection
Microdisplay Inspection: Color, relative intensity, spectroscopy and film thickness of pixels and light sources.
Microdisplays consist of a series of colored lighted areas arranged in a pattern and can only be readily viewed with magnifying optics. They are used as high resolution displays for everything from mobile phones to video display headgear to MP3 players. There are many different designs but their small scale causes many quality control challenges.
Due to the nature of microdisplays, they are manufactured with hundreds of rows of microscopic "pixels" on a surface. These pixels can be smaller than 10 microns across. Quality control of both the components and completed microdisplays is done by optical microspectroscopy. Microspectrometers, such as those made by CRAIC Technologies, are used to measure the color and the intensity of the output from individual pixels and from groups of pixels. In fact, CRAIC microspectrometers can be used to map the color and intensity outputs of individual pixels in addition to the entire microdisplay. This is important as manufacturers of microdisplays need to make sure that all the different types of pixels are the same color and brightness. A microspectrophotometer does this quickly and easily.
To learn more about microdisplay testing:
What is a Microspectrophotometer?
SWIR Microscopy
Discover the Unseen with SWIR Microscopy.
SWIR microscopy extend your capabilities far beyond those of standard optical microscopes. Equipped with specialized optics, light sources, and cameras, they can image samples in both the visible and shortwave infrared (SWIR) regions. This advanced imaging technology offers distinct advantages over conventional microscopes:
- Material Transparency: Some materials opaque in the visible spectrum become transparent in the SWIR range.
- Enhanced Contrast: Certain materials exhibit greater contrast in the SWIR region.
For instance, silicon, which is opaque under normal light, becomes transparent in the SWIR region, allowing for the inspection of silicon-based device interiors without disassembly.
CRAIC Technologies provides tailored solutions for SWIR microscopy. These custom-designed microscopes can image across the visible to shortwave infrared spectrum and perform microscopy in transmission, reflectance, and fluorescence. Unlock new possibilities with SWIR microscopy.
Learn more about SWIR microscopy:
SWIR Microscope
Discover the Unseen with CRAIC Technologies SWIR Microscopes
SWIR microscopes extend beyond the capabilities of standard optical microscopes. Equipped with specialized optics, light sources, and cameras, they can image samples in both the visible and shortwave infrared (SWIR) regions. This advanced imaging technology offers distinct advantages over conventional microscopes:
- Material Transparency: Some materials opaque in the visible spectrum become transparent in the SWIR range.
- Enhanced Contrast: Certain materials exhibit greater contrast in the SWIR region.
For instance, silicon, which is opaque under normal light, becomes transparent in the SWIR region, allowing for the inspection of silicon-based device interiors without disassembly.
CRAIC Technologies provides tailored solutions for SWIR microscopy. These custom-designed microscopes can image across the visible to shortwave infrared spectrum and perform microscopy in transmission, reflectance, and fluorescence. Unlock new possibilities with SWIR microscopy.
Learn more about SWIR microscopes: